Although operational auditing plays an important role in improving business performance, many companies do not fully understand its essence.
This is due to its similarity with internal audit, so there is often a misinterpretation between the two. In fact, an operational audit is more than just a financial audit.
An operational audit involves a comprehensive evaluation of the entire system, processes, and operations to help the company achieve its business objectives.
Therefore, let's see what operational audit is and its role in the business world!
Understanding Operational Audit
Operational Audit is the process of a thorough evaluation of the systems, operations, and processes that run in a company.
This process aims to assess the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall business performance. Hopefully, the company can identify which areas need improvement.
In this audit, every operational aspect, from internal policies, procedures, to controls, will be comprehensively examined.
Evaluation conducted by auditor team who have expertise in analyzing business processes in depth so as to support effective improvement.
Operational Audit Objectives
In addition to those already mentioned, this assessment has objectives in its application, namely:
- Find areas that require further improvement to achieve effective operation of a business.
- Analyze the optimal use of resources such as raw materials, equipment, and labor.
- Ensure compliance with existing regulations and laws.
- Assessing effectiveness risk management and internal controls are already implemented.
- Provide feedback to the company regarding holistic performance improvement.
From these explanations, the operational assessment aims to strengthen the efficiency and competitiveness of the company.
Types Of Operational Audits
Although evaluating the business as a whole, operational audits can be categorized into several types viz.
1. Information Technology Audit
IT Audit evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of the system and IT infrastructure, including data security, network performance, software utilization, and IT governance.
2. Financial Audit
Financial Audit focuses on the accuracy and reliability of the company's financial records. This process can inform the company's compliance with applicable financial standards.
3. Audit Department
In this audit, checks are carried out by targeting specific departments such as the human resources, procurement, or production departments.
Its purpose is to identify operational inefficiencies and improve the performance of the departments examined.
4. Marketing Audit

This type of assessment aims to evaluate the company's marketing strategies, campaigns and activities. Aspects that are evaluated is the effectiveness of marketing strategies and the level return of investment.
5. Compliance Audit
Related operational checks a compliance audit ensure the company operates in accordance with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. The Auditor will review policies, procedures, and practices to reduce the risk of non-compliance.
6. Investigative Audit
This Audit is carried out when there is a suspicion of fraud or irregularities. An in-depth examination will be carried out of the financial records and activities of the employees.
7. Follow-Up Audit
A follow-up Audit is conducted after the previous audit to assess the effectiveness of implementing the recommendations that have been given and ensure continuous improvement.
Operational Audit Example
To give you a better idea, we summarize some examples of operational audits that deliver real-world business success.
1. Operational Audit Example 1
PQR manufacturing companies conduct operational assessments to find inefficiencies in the production process.
These audits uncover bottlenecks in the supply chain and opportunities to improve inventory management.
By implementing the audit recommendations, PQR managed to lower production costs, optimize inventory, and improve operational efficiency.
2. Operational Audit Example 2
ABC retail company held this practice to assess the customer service process.
These audits revealed long wait times, less effective communication channels, as well as inadequate training of customer service staff.
After implementing the recommendations, ABC was able to speed up response times, improve communication with customers, and increase customer satisfaction and retention.
3. Operational Audit Example 3
XYZ technology companies conduct operational assessments to evaluate IT infrastructure and data security.
This Audit found weaknesses in network security, data backup protocols, and disaster recovery plans.
By following the audit recommendations, XYZ succeeded in improving data protection, reducing the risk of cyberattacks, and ensuring system availability and integrity.
Lack Of Operational Audit
Although this practice can favor business success, it is necessary to know that this process also has some drawbacks that need to be anticipated and mitigated in its execution.
1. Cost Of Audit

Operational audits can require significant costs, both if carried out by audit team internal or by using the services of external auditors.
This cost includes the preparation, conduct, as well as follow-up of the audit itself.
2. Required duration
The audit process often takes a while, especially if the audit is carried out in a company with a complex structure and many departments that need to be checked.
This time also has the potential to interfere with daily business activities.
3. Potential conflicts with management
Sometimes, audits can cause conflicts, especially if the results of the audit and its recommendations are not in line with management's expectations.
Auditors need to maintain a professional and independent attitude in dealing with situations like this.
4. Difficulty connecting with business goals
In some cases, auditors may have difficulty associating the audited process with key business objectives.
This can be due to a poorly defined goal formulation or the complexity of the examined business processes.
These deficiencies must be addressed so that operational audits can run effectively and provide added value to the company.
Stages Of Operational Audit
For those of you who are interested in implementing an operational audit, the following tahapan audit all you have to do.
- Determination Of Auditors: Auditors can be appointed internally or hired external auditor.
- Audit Process Planning: Once determined, the auditor discusses with the relevant managers to plan the appropriate audit methods, scope , schedule, objectives, and strategies.
- Audit Implementation: Auditors evaluate business areas by assessing processes, discussing, and making observations. Afterwards the auditor designs tests to find areas that need improvement.
- Reporting Audit Findings: In this process, the auditor prepares a report on the findings and recommendations for improvement and discusses them with management.
- Follow-Up: After the audit is complete, the auditor schedules a follow-up meeting about six months later to evaluate the results of the changes as well as measure achievement.
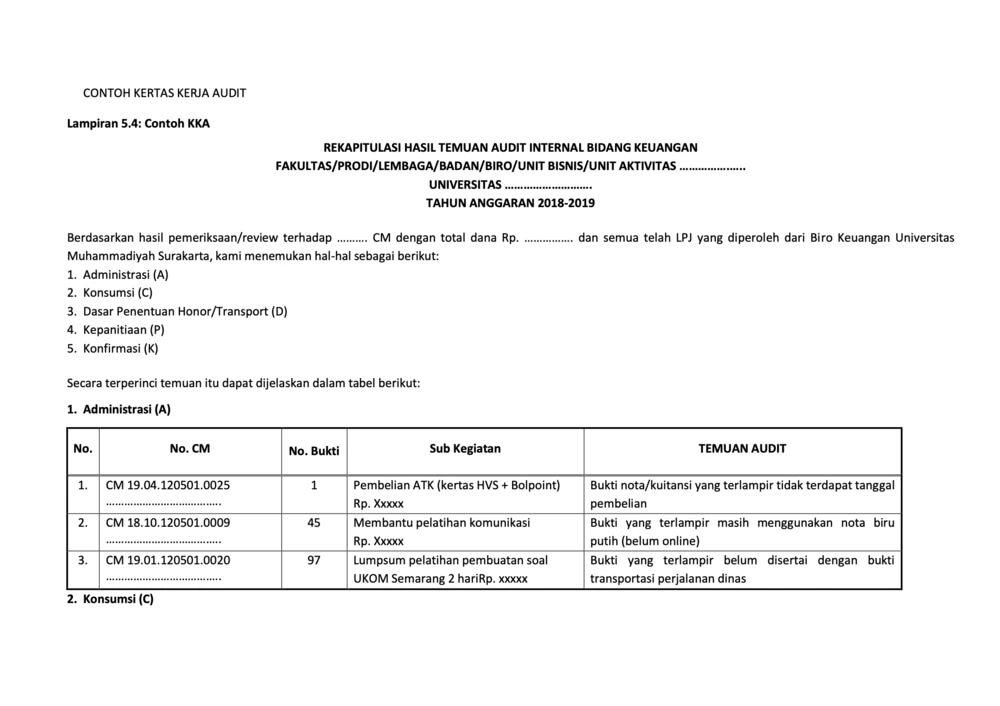
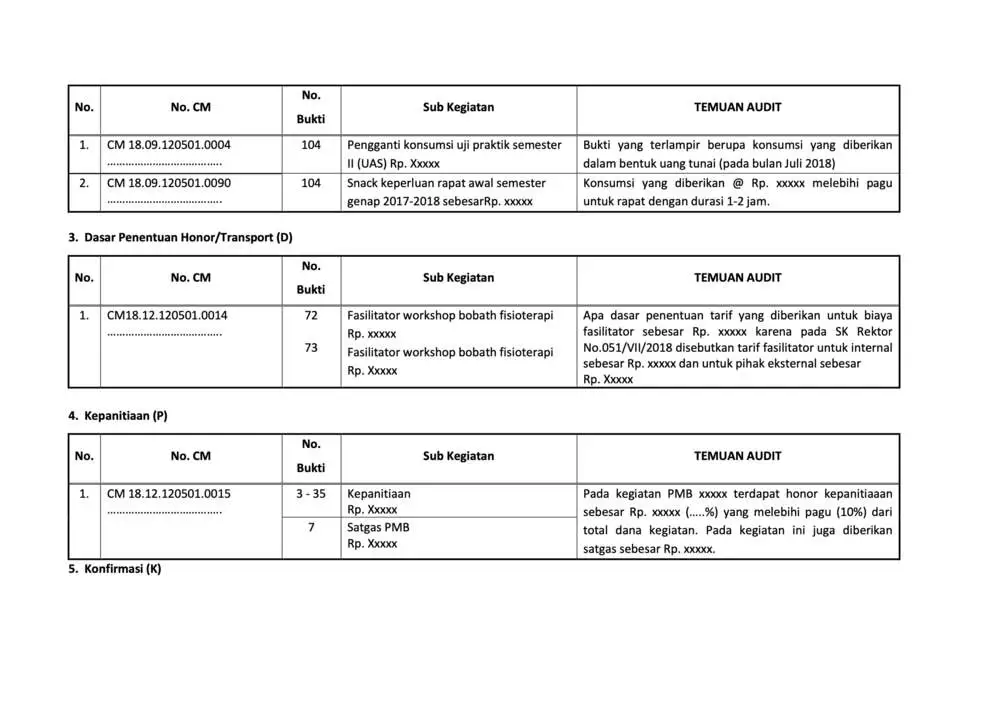
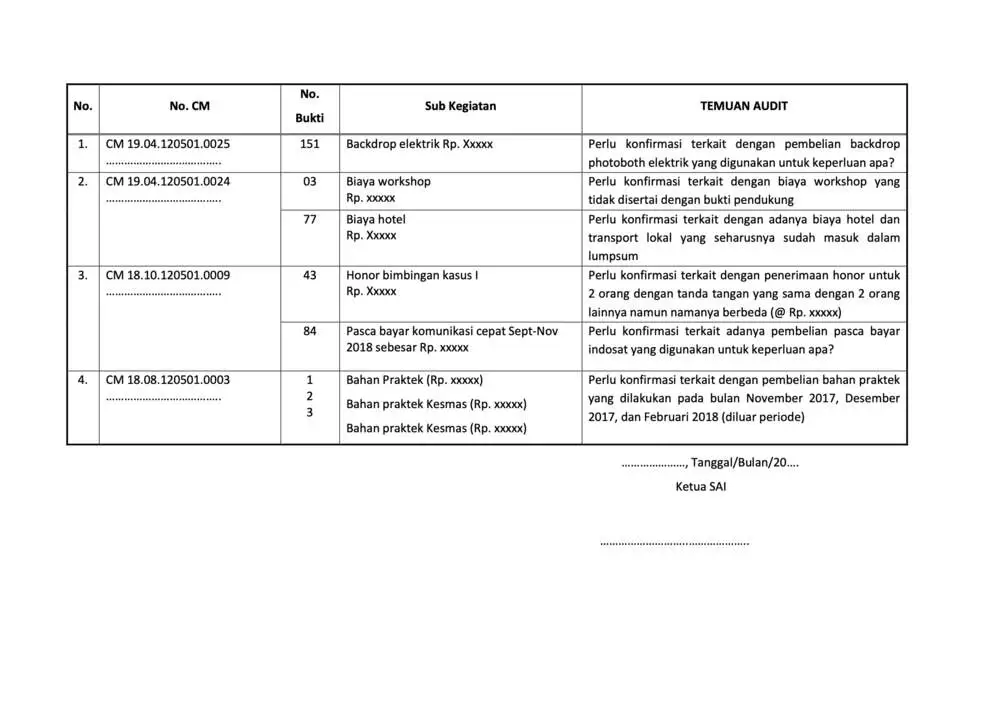
Examples Of Operational Audit Working Papers
To conduct an operational audit, it takes audit working papers as a documentation tool that records all of the auditor's findings, analysis, and recommendations during the audit process.
Here we present some examples as a reference.
Conclusion
Operational Audit is an important process to improve business efficiency and effectiveness,
By conducting a thorough evaluation of systems and processes, operational audits help the company achieve its goals.
Involve Audithink's Comprehensive Features in the process of auditing your company's operations.
With Audithink, the audit process will become more efficient, structured, and easier to identify problems.
Try application demo for free!




